Hello tech enthusiasts, welcome back to my latest blog post on bittutech.com!
A Beginner’s Guide :-
In today’s digital age, computers have become an integral part of our daily lives. From simple tasks like browsing the internet to complex tasks like data analysis and software development, computers have revolutionized the way we work, communicate, and entertain ourselves.
In this blog post, we will provide a brief introduction to computers, covering the basics of what a computer is, its components, and its uses.
What is Computer ?
Table of Contents

The word ‘Computer’ is derived from the word ‘compute’, which means ‘calculation’. A computer is an electronic device that can store, process, and communicate information. It is a machine that can perform tasks automatically, following a set of instructions called a program.
Types of Computer
Computer has been categorized into following parts :-
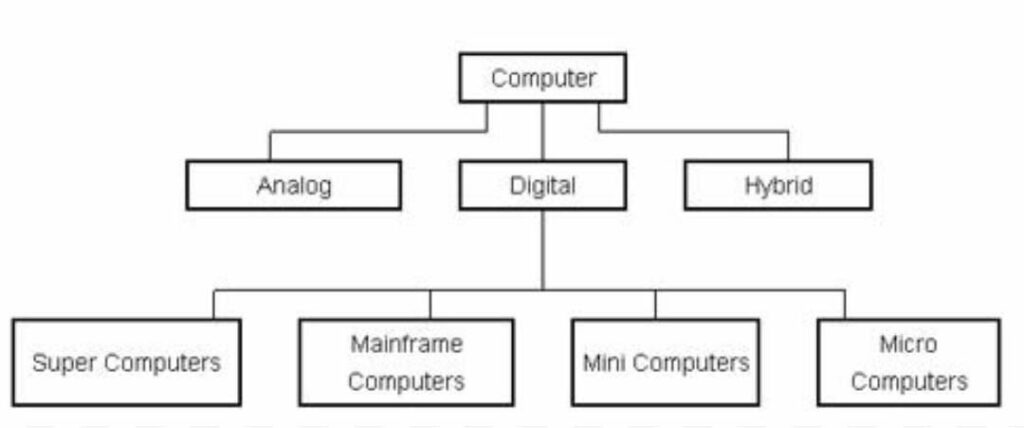
- Analog Computer:- An analog computer is a type of computer that uses continuous signals or physical phenomena to perform calculations and solve problems. Analog computers use continuous values, such as voltages, currents, or pressures, to represent and manipulate data.
- Digital Computer:- A digital computer is a type of computer that uses discrete values, such as 0s and 1s, to represent and manipulate data. Digital computers are based on the binary number system, which uses only two digits: 0 and 1.
- Micro Computer:- Micro computer is single user device. example, Desktop, Laptop, Palmtop, Notepad etc.
- Mini Computer:- Mini Computer is multi user device generally used in designing company for commercial use.
- Mainframe Computer:- Number of users is more than Mini Computer. This is multi-user and multi-tasking device, mostly used in Metrology.
- Super Computer:- The processor is biggest than other Computer and processing capacity is highest than other devices. It is multi-user fastest calculating device, generally used in nuclear science for calculation purpose.
3. Hybrid Computer:- This type of computer comes with both characteristics (digital and analog) are called hybrid Computer.
Characteristics of Computers
- Speed:- Computer can perform any types of work with greatest speed. It takes only few second for calculation that we take hours to complete.
- Accuracy:- Computer can do calculation without errors and very accurately.
- Diligence:- The computer can perform any task continuously without getting tired.
- Storage Capacity:- Computer can store large volume of data and information on magnetic media. The computer has an in-built memory where it can store a large amount of data.
- Versatility:- Computers are versatile. They perform multiple different task at the same time.
Basic Applications of Computers
- Word Processing:- Word Processing software help us to do our day to day work smoothly like letter typing, making resume, etc.
- In banking:- Now-a-days Net Banking is become popular.
- Internet:- You can connect your computer to any computer anywhere either in India or abroad. It is a global system to interconnected computer network.
- Hospital:- In hospital you will see that the records of patients related to name of patients, disease, etc are stored in computer.
- Communication:- Computers let the people communicate with each other through chatting, video calling, e-mail, e learning, etc.
History of Computer
- Charles Babbage (1822):- Proposed the idea of a mechanical computer, the Difference Engine.
- Ada Lovelace (1843):- Wrote the first computer program for Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine.
- Konrad Zuse (1936):- Built the first electronic computer, the Z1.
- John Atanasoff (1939):- Developed the first electronic computer with a binary system, the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC).
- ENIAC (1946):- The first general-purpose electronic computer, developed by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert.
Generations of Computer
First Generation (1940s-1950s) :-
- Vacuum Tubes:- Used as the primary electronic components.
- Machine Language:- Programs were written in machine language, which consisted of 0s and 1s.
- Punch Cards:- Input was provided using punch cards.
- Magnetic Drums:- Used for storage.
- Examples:- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), UNIVAC 1.
Second Generation (1950s-1960s) :-
- Transistors:- Replaced vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable.
- Assembly Language:- Programs were written in assembly language, which used symbolic codes.
- Magnetic Tapes:- Used for storage.
- Examples:- IBM 7090, CDC 1604.
Third Generation (1960s-1970s) :-
- Integrated Circuits (ICs):- Replaced transistors, further increasing speed and reducing size.
- High-Level Languages:- Programs were written in high-level languages, such as COBOL and FORTRAN.
- Operating Systems:- Introduced to manage computer resources.
- Examples:- IBM System/360, PDP-8.
Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s) :-
- Microprocessors:- Integrated all components of a computer onto a single chip.
- Personal Computers:- Emerged, making computers accessible to individuals.
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs):- Introduced, making computers easier to use.
- Examples:- Apple II, IBM PC.
Fifth Generation (1980s-1990s) :-
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):- Became a focus area, with the development of expert systems and natural language processing.
- Parallel Processing:- Introduced, allowing computers to perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
- High-Performance Computing:- Emerged, with the development of supercomputers.
- Examples:- Apple Macintosh, IBM PS/2.
Sixth Generation (1990s-present) :-
- Internet and World Wide Web:- Revolutionized the way computers are used, with the emergence of online services and e-commerce.
- Mobile Devices:- Emerged, with the development of laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
- Cloud Computing:- Introduced, allowing users to access computing resources over the internet.
- Big Data and Analytics:- Became a focus area, with the development of data mining and machine learning techniques.
- Examples:- Modern smartphones, laptops, and cloud computing services.
IT Gadgets and their applications
- Smart Watch :- Smart watches can run apps and play back all sorts of digital media, like audio tracks or radio streamed to Bluetooth headphones and also allow to access functions like calculator, thermometer, compass and more like Smart Phones.
- Google glass :- Google Glasses is wearable, voice-controlled Android device that resembles a pair of eye glasses and display information directly in the user’s field of vision.
- PDAs (Personal Digital Assistance) :- Personal Digital Assistance (PDA) is a handheld computer that fits in the palm of your hand to help collect such information as contacts, appointments, files, and programs. PADs may also known as Palmtop, hand held computer or pocket computer.
- Drone Camera:- A drone is “An unmanned aircraft or ship that can navigate autonomously, without human control or beyond the line of sight”.
- Pen with Camera:- Simply put, a spy pen is an ordinary pen with a hidden digital digital camera concealed inside, allowing the use to take covert video, often with the pen placed in the shirt pocket or held in the hand.
What is Hardware?
Hardware refers to the physical components of computer that we can see as well as touch. For Example Keyboard, Mouse, CPU, Memory and Storage devices.
What is Software ?
Software is a set of instructions, data or programs used to operate computer and execute specific tasks.
Software can be divided in two parts..,
- System Software :- This controls a computer’s internal functioning through an operating system, and also such peripherals.
- Application Software :- This is used by users to accomplish specific tasks.
NOTE :- The boundary between Hardware and Software is connected through Firmware Software that is built-in to the hardware.
What is Operating System?
An operating system (OS) is a software that manages and control the hardware and software resources of a computer, providing a platform for running applications and managing computer resources. it acts as an intermediary between the user and the computer hardware.
Examples of Operating Systems:
- Windows; Developed by Microsoft.
- macOS: Developed by Apple.
- Linux: Open-source operating system.
- Android; Developed by Google for mobile devices.
- iOS: Developed by Apple for mobile devices.
What is Peripheral Devices ?
Peripheral devices are hardware components that connect to a computer system to provide additional functionality, enhance performance, or expand the system’s capabilities. These devices are not part of the central processing unit (CPU) or main memory, but rather external components that interact with the computer.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the primary component of a computer that perform most of the processing inside a computer. It is often referred to as the “Brain” of the computer.
Key Functions of a CPU:-
- Executing Instructions:- The CPU takes in instructions from the operating system and applications, decodes them, and carries out the required actions.
- Performing Calculations:- The CPU performs mathematical and logical calculations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Managing Data:- The CPU moves data between different parts of the computer, such as the memory and input/output devices.
- Controlling Operations:- The CPU manages the flow of data and instructions between different parts of the computer.
Components of a CPU:-
- Control Unit:- Retrieves instructions, decodes them, and manages the flow of data.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):- Performs mathematical and logical calculations.
- Registers:- Small amounts of memory built into the CPU to store data temporarily.
- Cache Memory:- A small, fast memory that stores frequently accessed data.
Types of CPUs:-
- Microprocessor:- A CPU that contains all the components on a single chip of silicon.
- Multi-Core Processor:- A CPU that contains multiple processing cores, allowing for multiple instructions to be executed simultaneously.
- Embedded Processor:- A CPU designed for use in embedded systems, such as traffic lights, appliances, and automotive systems.
Types of Processing
- Serial Processing :- Execute one instruction at a time; Fetch, Decode and Execute.
- Parallel Processing :- Multiple processes are done at the same time.
- Pipeline Processing :- A technique is which the processer begins executing a second instruction before the first has been completed. Thus several instructions can be executed simultaneously, each at a different processing stage.
Input Devices
An input device is a hardware component that allows users to interact with a computer system and provide data, instructions, or commands. Input devices enable users to communicate with the computer, and they play a crucial role in the overall functionality of the system.
Some Input Devices :-
- Keyboard:- A keyboard is the most common input device, allowing users to type text, numbers, and symbols.
- Mouse:- A mouse is a pointing device that enables users to interact with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and select items on the screen.
- Scanner:- A scanner is an input device that converts printed or handwritten text into digital format.
- Microphone:- A microphone is an input device that captures audio signals, allowing users to record voice messages, participate in video conferencing, or interact with voice assistants.
- Webcam:- A webcam is an input device that captures video and images, enabling users to participate in video conferencing, take photos, or record videos.
- Gamepad:- A gamepad is an input device designed for gaming, providing users with a convenient way to control games and interact with virtual environments.
- Touchscreen:- A touchscreen is an input device that allows users to interact with a computer system by touching the screen.
- Barcode Reader:- A barcode reader is an input device that scans barcodes and converts them into digital data.
- Fingerprint Reader:- A fingerprint reader is an input device that captures fingerprint data, enabling users to authenticate and access secure systems.
- Voice Recognition System:- A voice recognition system is an input device that uses speech recognition technology to convert spoken words into digital text.
Functions of Input Devices:-
- Data Entry:- Input devices enable users to enter data, such as text, numbers, and symbols, into a computer system.
- Command Input:- Input devices allow users to provide commands, such as mouse clicks or keyboard shortcuts, to interact with a computer system.
- Navigation:- Input devices, such as mice and touchscreens, enable users to navigate through graphical user interfaces and select items on the screen.
- Authentication:- Input devices, such as fingerprint readers and voice recognition systems, provide secure authentication methods to access computer systems.
Output Devices
An output device is a hardware component that receives data from a computer system and presents it in a human-readable or audible format. Output devices enable users to view, hear, or otherwise perceive the results of computer processing.
Some Output Devices:-
- Monitor:- A monitor displays visual output, such as text, images, and videos.
- Printer:- A printer produces hardcopy output, such as printed documents and images.
- Speakers:- Speakers produce audio output, such as music, voice, and sound effects.
- Headphones:- Headphones produce audio output, providing a personal and immersive listening experience.
- Projector:- A projector displays visual output onto a larger screen or surface.
- Plotter:- A plotter produces graphical output, such as charts, graphs, and diagrams.
- Braille Display:- A Braille display produces tactile output, enabling visually impaired users to read text.
- LED Display:- An LED display produces visual output, often used for displaying numeric or alphanumeric data.
Functions of Output Devices:-
- Displaying Data:- Output devices present data in a human-readable or audible format.
- Printing Documents:- Printers produce hardcopy output, such as printed documents and images.
- Producing Audio:- Speakers and headphones produce audio output, such as music, voice, and sound effects.
- Presenting Visuals:- Monitors, projectors, and plotters display visual output, such as text, images, and videos.
- Providing Tactile Feedback:- Braille displays and other tactile output devices enable visually impaired users to interact with computers.
Computer Memory and Storage
It is an internal storage area in computer system. The memory is used for physical memory which refers to the actual chips capable of holding data There is also a virtual memory, which expands physical memory onto a hard disk. The term Memory can be categorized in two parts Primary Memory and Secondary Memory.
Primary Memory
Primary memory, also known as main memory or internal memory, is a type of computer memory that stores data and program instructions temporarily while a computer is running. It is called “primary” because it is the main memory that the computer uses to perform calculations and execute instructions.
Functions of Primary Memory :-
- Data Storage:- Primary memory stores data temporarily while the computer is running.
- Instruction Storage:- Primary memory stores program instructions temporarily while the computer is running.
- Cache Memory:- Primary memory can also serve as a cache memory, storing frequently accessed data and instructions for fast access.
Types of Primary Memory:-
1. RAM (Random Access Memory):- RAM is the most common type of primary memory. It is a volatile memory technology that stores data temporarily while the computer is running.
Types of RAM :-
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
DRAM is the most common type of RAM used in modern computers. It stores data in capacitors, which must be periodically refreshed to maintain the data. - SRAM (Static RAM)
SRAM is a type of RAM that stores data in flip-flops, which do not require refreshing. SRAM is faster and more expensive than DRAM. - SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)
SDRAM is a type of DRAM that synchronizes its operations with the system clock. SDRAM is faster than traditional DRAM. - DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM)
DDR SDRAM is a type of SDRAM that transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. DDR SDRAM is faster than traditional SDRAM. - DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM is a type of DDR SDRAM that operates at higher speeds and has lower power consumption. - DDR3 SDRAM
DDR3 SDRAM is a type of DDR2 SDRAM that operates at even higher speeds and has lower power consumption. - DDR4 SDRAM
DDR4 SDRAM is a type of DDR3 SDRAM that operates at higher speeds and has lower power consumption. - DDR5 SDRAM
DDR5 SDRAM is the latest generation of DDR SDRAM, offering even higher speeds and lower power consumption. - RDRAM (Rambus DRAM)
RDRAM is a type of DRAM that uses a high-speed bus to transfer data. RDRAM was used in some early 2000s computers. - XDR DRAM (Extreme Data Rate DRAM)
XDR DRAM is a type of DRAM developed by Rambus, offering high-speed data transfer rates. - FB-DIMM (Fully Buffered DIMM)
FB-DIMM is a type of DRAM module that uses a buffer chip to improve signal integrity and increase memory capacity. - SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM)
SO-DIMM is a type of DRAM module used in laptops and other small form factor computers. - ECC RAM (Error-Correcting Code RAM)
ECC RAM is a type of RAM that includes error-correcting code to detect and correct data errors. - Registered RAM
Registered RAM is a type of RAM that uses a register chip to buffer the data and address signals. - Unbuffered RAM
Unbuffered RAM is a type of RAM that does not use a buffer chip, offering lower latency and lower cost.
2. ROM (Read-Only Memory):- ROM is a type of primary memory that stores data permanently. It is used to store firmware, such as the computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
Types of ROM :-
- Masked ROM (MROM)
MROM is the most basic type of ROM, where the data is programmed during the manufacturing process. - Programmable ROM (PROM)
PROM is a type of ROM that can be programmed by the user using a special device called a PROM programmer. - Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM)
EPROM is a type of ROM that can be erased and reprogrammed using ultraviolet light. - Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM)
EEPROM is a type of ROM that can be erased and reprogrammed using an electrical signal. - Flash ROM
Flash ROM is a type of ROM that can be erased and reprogrammed using a special device called a flash programmer. - One-Time Programmable ROM (OTP ROM)
OTP ROM is a type of ROM that can be programmed only once. - Field-Programmable ROM (FPROM)
FPROM is a type of ROM that can be programmed in the field using a special device. - Fuse-Programmable ROM (FUSE ROM)
FUSE ROM is a type of ROM that uses fuses to store data. - Phase-Change Memory ROM (PCMR)
PCMR is a type of ROM that uses phase-change memory to store data.
Secondary Memory
Secondary memory, also known as external memory or non-volatile memory, is a type of computer memory that stores data and program instructions permanently, even when the computer is powered off. It is called “secondary” because it is not directly accessible by the computer’s processor, unlike primary memory (RAM).
Functions of Secondary Memory:-
- Data Storage:- Secondary memory stores data permanently, even when the power is turned off.
- Program Storage:- Secondary memory stores program instructions permanently.
- Backup Storage:- Secondary memory can be used for backup purposes, storing copies of important data and programs.
Types of Secondary Memory :-
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD):- A non-volatile storage device that stores data on a magnetic disk.
- Solid-State Drive (SSD):- A non-volatile storage device that stores data on interconnected flash memory chips.
- Flash Drive:- A small, portable storage device that stores data on flash memory.
- CD/DVD/Blu-ray Drive:- An optical storage device that stores data on discs.
- Magnetic Tape Drive:- A storage device that stores data on magnetic tape.
Mobile Application
A mobile app, also known as a mobile application, is a software application designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. Mobile apps are typically downloaded from app stores, such as Apple App Store or Google Play, and installed on the device.
Characteristics of Mobile Apps :-
- Portability:- Mobile apps are designed to be portable and can be used on-the-go.
- User-friendly:- Mobile apps are designed to be intuitive and easy to use.
- Touch-based interface:- Mobile apps use a touch-based interface, allowing users to interact with the app using gestures such as tapping, swiping, and pinching.
- Internet connectivity:- Many mobile apps require internet connectivity to function, allowing users to access online services and data.
Benefits of Mobile Apps :-
- Convenience:- Mobile apps provide users with convenient access to information and services on-the-go.
- Personalization:- Mobile apps can be personalized to meet the individual needs and preferences of users.
- Improved productivity:- Mobile apps can help users manage their time and increase their productivity.
- Enhanced user experience:- Mobile apps can provide users with an enhanced user experience, using features such as touch-based interfaces and location-based services.
Here is the list of some most important Mobile Application :-
- Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) App :- The app is a Unified Payment Interface (UPI) and was developed by National Payment Corporation of India. It has been named after Bhim Rao Ambedkar and is intended to facilitate e-payment directly through banks and as per of the 2016 Indian banknote demonetization and drive towards cashflow transactions. Currently a maximum of Rs. 10,000 per transaction is allowed.
- MyGov App :- This app is a citizen engagement platform founded by the Government of India to promote active participation of Indian citizens in country’s governance and development.
- IRCTC Connect App :- The Indian Railways had recently launched an android app to make the ticket booking easier for the people. Whit the help of this app, User can search and book train tickets, user can view and cancel tickets, New user can register from the app directly.
- DigiLocker App :- DigiLocker is a “Digital Locker” service operated by the Government of India that enable Indian citizen to store certain official documents on the cloud.
- Voter Help Line App :- Taking forward its continuous efforts of building an active democratic citizen in the country. Election Commission of India has undertaken a new initiative by designing a mobile app for developing a culture of avid electoral engagement and making informed and ethical ballot decision among citizen of the country. The app aims to provide a single plateform for service and information delivery to voter across the country.
- GARV (Grameen Vidyutikaran) App :- This app let anyone track the progress of rural electrification in India through a real-time dashboard. Report by the GVAs (Grameen Vidyut Abhiyantas and rural electrification engineers) are shared through the GARV app with officials as well as the public.
- mPassport Seva :- Passport seva project, being executed by Consular, Passport and Visa (CPV) division of Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Government of India, aims to providing all the Passports related services of Indian citizen in the speedy, convenient and transport manner. This is one of the largest project of Government of India under the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) being executed in public-private partnership mode with Tata Consultancy Service (TCS) as the private partner.
- OnlineRTI – File RTI Online :- RTI – Right to Information Act allow any citizen to get information from the government RTI act is applicable to all 29 states and 8 union territories.
“Begin with the basics, and you’ll soon realize that the possibilities are endless.” ~ Prajjwal Singh (Tech Blogger)